- Resonance
- Posts
- 🔵 The Quantum Insider Weekly | GiANT Round. Of Tetron and Topological. And More News.
🔵 The Quantum Insider Weekly | GiANT Round. Of Tetron and Topological. And More News.

Was this email forwarded to you? Subscribe below to never miss a qubit. 👇️
FROM THE EDITOR.
To level set on my ability to predict trends, please remember that you are talking to the guy who said in 1982 that The Alarm would be bigger than U2. Having said that, the growing appetite for investing in quantum appears to be more than a coincidence.
This week, Q.ANT, a German photonics company, announced a €62 million Series A round—an unusually large figure for an initial institutional raise. Meanwhile, SandboxAQ reported an additional $95 million in financing, further elevating its already substantial valuation, now exceeding $5 billion.
It is also worth recognizing several other notable fundraises this week. Bifrost Electronics, a Colorado-based quantum readout startup, closed a $2.5 million seed round, reinforcing the strength of the regional ecosystem in the U.S. Mountain West. BQP, another early-stage company, announced an oversubscribed $4.9 million seed raise. In India, QpiAI secured funding that adds momentum to the country’s rapidly maturing quantum landscape.
These announcements represent only a portion of the capital flowing into the sector over the past week.
Why do I think this is more than a coincidence? While fundamentals such as solid leadership, technical innovation, and market potential remain central to investor calculus, there may also be heightened attention on companies that bridge quantum with artificial intelligence—two domains experiencing simultaneous waves of transformative change.
I conclude with Sixty Eight Guns featuring Mike Peters, who we recently lost in the spring to cancer.
Have a great weekend!
— Matt, Chief Content Officer at The Quantum Insider
INSIDER BRIEF.
ANALYST NOTES.
The Noteworthy & Nuanced
Lots of funding this week! SandboxAQ is providing employee liquidity by raising $95M in an oversubscribed secondary offering. The company is advancing Large Quantitative Models (LQMs) for use in defense, energy, and biopharma sectors. Lead backers include Rizvi Traverse, Forge Global, and the Ava Family Office, who called out SandboxAQ for its unique approach to cybersecurity, drug discovery, and quantum simulation.
Q.ANT absolutely qan secure funding - €62M in Series A funding to commercialize its cutting-edge photonic processors. Built on Thin-Film Lithium Niobate, the processors aim to transform AI and high-performance computing, particularly amid surging data center power demands. Backed by Cherry Ventures, UVC Partners, and imec.xpand, Q.ANT will expand globally and integrate its Native Processing Server into major data centers.
Lastly, QpiAI has raised $32M in Series A funding led by Avataar Ventures and India’s National Quantum Mission to expand its global quantum computing platform. With proprietary hardware and software, QpiAI delivers enterprise-grade solutions in drug discovery and materials science. Headquartered in India, it also operates in Finland and the US. — Alan Kanapin, Analyst at The Quantum Insider
The Research Rundown
This week’s research stories live somewhere in the outer limits of what quantum can solve, from infinite search spaces to fundamental physics simulations.
Researchers from TRIUMF and the Perimeter Institute combined deep learning and quantum computing to simulate particle collisions more efficiently, addressing one of high-energy physics’ biggest computational bottlenecks. Using D-Wave’s quantum technology, the team built a generative model that could reduce simulation time and cost ahead of the LHC's next major upgrade.
Meanwhile, a team led by Chalmers University made headway on a different kind of bottleneck — verification. Their new algorithm is the first to enable classical simulation of quantum circuits that use Gottesman-Kitaev-Preskill bosonic codes. Simulating these codes on classical machines was previously intractable, making this a notable step toward testing and validating quantum systems before they scale.
Finally, researchers in China have extended Grover’s algorithm into the continuous domain, developing a quantum search method that retains quadratic speedup even across infinite solution spaces.
With rigorous proofs of optimality and a general oracle construction framework, this could become foundational for quantum approaches to high-dimensional optimization, spectral analysis, and continuous-variable quantum computing. — Cierra Choucair, Journalist & Analyst at The Quantum Insider
Want more research insights? Get them delivered straight to your inbox Monday, Wednesday, and Friday with The Daily Qubit. Subscribe below or use the link to update preferences at the end of this email. 👇️
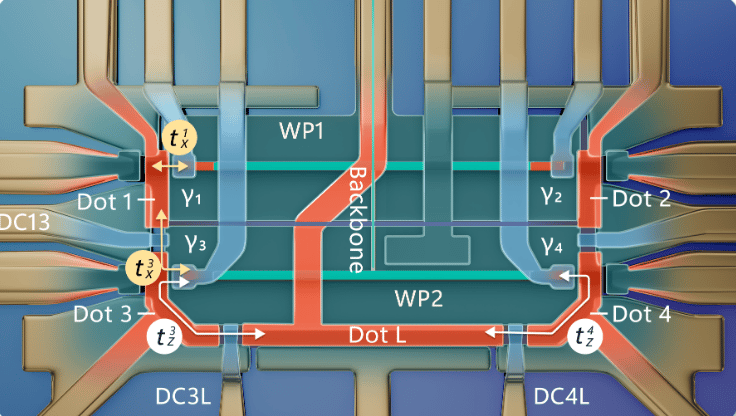
INSIDER SPOTLIGHT: Microsoft Shows Distinct Parity Lifetimes in Topological Qubit Prototype
➡️ Microsoft has demonstrated two distinct, projective quantum measurements — Pauli-X and Pauli-Z — in a prototype tetron qubit device, showing vastly different lifetimes for each and advancing its effort to build scalable topological quantum computers.
➡️ The experiment measured 14.5 microseconds for the X-basis and 12.4 milliseconds for the Z-basis, a three-order-of-magnitude gap that reflects different sources of quantum decoherence and supports Microsoft’s interpretation of Majorana behavior.
➡️ While the results are consistent with a topological qubit model, the researchers caution that non-topological systems could mimic some of the observed signatures, and more work is needed to eliminate alternative explanations.
➡️ The team’s next milestone is to demonstrate non-commuting X and Z measurements, a requirement for full quantum logic and a step toward Microsoft’s long-term goal of fault-tolerant, Majorana-based quantum computing.
Analyst Commentary
Microsoft’s newly released tetron study represents a measured but meaningful step forward in what many experts consider its high-stakes pursuit of topological quantum computing. Published on arXiv, the work demonstrates a prototype device capable of reliably distinguishing between Pauli-X and Pauli-Z measurements. Why is that important? It’s a fundamental requirement for any quantum system that aims to compute by measurement rather than control pulses.
At the heart of the experiment is the tetron layout: a hybrid semiconductor-superconductor structure that hosts four Majorana zero modes, arranged to encode one logical qubit. The team found that measuring quantum parity along the Z loop produced remarkably stable results, with parity switches occurring only every 12.4 milliseconds on average — a figure attributed to quasiparticle poisoning from external disturbances. In contrast, the X loop flipped far more quickly, every 14.5 microseconds, reflecting more subtle internal dynamics like energy splitting between Majorana pairs.
These results aren’t just about speed — they’re about fidelity. The Z measurement achieved a low assignment error of ~0.5%, while the faster X measurement had a 16% error rate. Microsoft researchers model these differences and the results suggest a strong grasp of the device’s underlying physics.
To their credit, the authors avoid overstating the results. While the measured behavior aligns with expectations for Majorana-based systems, the paper notes that certain non-topological devices — under finely tuned conditions — could in theory produce similar signatures. Rather than declaring victory, Microsoft has chosen to publish data that answers some past criticisms while openly acknowledging the need for further verification.
The team outlines a path forward. Their next objective is to execute back-to-back X and Z measurements to test whether the operations truly don’t commute — a definitive test of quantum logic. If successful, this would strengthen the case that the tetron architecture can support universal, fault-tolerant quantum computation using topological protection.
The long-term vision is ambitious: a scalable quantum platform with fewer error-correction demands than rival approaches. But challenges remain. The relatively high error rate for the X basis must be lowered through improved materials and tighter control over energy splitting. Future iterations will likely involve better magnetic shielding, shorter coherence lengths, and more robust fabrication techniques to increase the topological energy gap.
This study might also be signal to the quantum ecosystem. While the industry often rewards announcements of “breakthroughs,” Microsoft’s work is a reminder that serious progress requires patience, rigorous testing, and an openness to critique. Publishing pre-peer-reviewed data with caveats intact is a sign of scientific maturity — and perhaps quiet confidence.
Microsoft has staked its quantum roadmap on topology, a path that is harder and slower than more conventional approaches. But if the company can continue to validate key milestones like these — and follow through on the non-commuting measurements and scaling roadmap — it may yet prove that its bet was the right one.
For now, the message is clear: progress is being made, but there is a lot of work left to do before the verdict comes in.
DATA SPOTLIGHT.

Physicists at the University of Oxford have set a new record for the accuracy of controlling a single quantum bit, achieving the lowest-ever error rate for a quantum logic operation—just 0.000015%, or one error in 6.7M operations. This record-breaking result represents nearly an order of magnitude improvement over the previous benchmark, set by the same research group a decade ago.
INDUSTRY HIGHLIGHTS.
🖥️ Terra Quantum has fabricated and validated the world’s first foundry-grade Negative Capacitance Field-Effect Transistor, a development that enables chips to run up to 40x faster and 20x more energy-efficient than current technologies.
🤝 The U.S. and Israel are planning a $200 million joint quantum and AI fund to launch in 2026, with a intention to strengthen regional alliances and counter China’s tech influence. With potential backing from Gulf states like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, the initiative would support collaborative R&D.
🔒️ Forward Edge-AI’s Isidore Quantum platform has achieved FIPS 140-3 certification, making it the first all-domain, quantum-resistant encryption system validated across air, land, sea, and space.
⚓️ Q-CTRL successfully demonstrated a fully autonomous quantum gravimetric navigation system during a 144-hour Royal Australian Navy trial, enabling GPS-free navigation by mapping Earth’s gravity.
✨ Universal Quantum Deutschland and Hamburg University of Technology have launched a multi-million Euro partnership to develop a next-generation programming interface for fault-tolerant quantum computing at the 100,000-qubit scale.
🚀 Sumitomo Corporation is accelerating real-world adoption of quantum computing through its Quantum Transformation Project, with pilot initiatives in logistics, drone traffic control, and mining optimization.
📐 Researchers from Cornell, IBM, Harvard, and the Weizmann Institute have achieved the first error-resistant implementation of universal quantum gates using the braiding of Fibonacci anyons, a notable development in fault-tolerant topological quantum computing.
✈️ SandboxAQ and Acubed have successfully demonstrated AQNav, an AI-powered quantum magnetic navigation system that enables real-time aircraft positioning without GPS, even under GNSS-denied conditions.
✅ Rigetti Computing has achieved 99.5% median two-qubit gate fidelity on its new modular 36-qubit chiplet-based system, an improvement over its previous Ankaa™-3 system. The company plans to launch the 36-qubit system on August 15 and is on track to deliver a 100+ qubit system with the same fidelity by the end of 2025.
💰️ Bifrost Electronics has raised $2.5 million in seed funding to advance its scalable, magnetically insensitive quantum amplifiers, designed to improve readout reliability and integration across various qubit platforms.
💸 SandboxAQ has raised $95 million in an oversubscribed secondary offering to provide employee liquidity, bringing its total funding to nearly $1 billion since its 2022 spinout from Alphabet
💰️ Qubitcore Inc. has secured pre-seed funding led by OIST Lifetime Ventures and signed an exclusive IP licensing agreement with the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology to commercialize a distributed ion-trap quantum computing architecture.
💸 BQP has raised an oversubscribed $4.9M seed round to scale its quantum-accelerated digital twin platform, BQPhy, designed for mission-critical simulations in aerospace, defense, and semiconductor industries.
🧊 Oxford Ionics has partnered with Iceberg Quantum to integrate quantum low-density parity-check codes into its trapped-ion hardware, aiming to reduce qubit overhead and accelerate the path to fault-tolerant quantum computing.
🧭 Denmark’s EIFO and the Novo Nordisk Foundation are investing €80M to establish QuNorth, a Nordic quantum initiative that will operate Magne, one of the world’s first commercial quantum computers based on logical qubits. Built by Atom Computing and Microsoft, Magne will be deployed in Copenhagen by early 2027.
🤝 Quobly and Inria have partnered to co-develop a fully integrated quantum computing architecture based on silicon qubits and tailored middleware and error correction protocols.
💰️ Commutator Studios has raised €1.5 million to develop its hardware-agnostic Quantum Error Management Platform, which uses AI to improve quantum software performance across all major platforms.
🇮🇳 QpiAI has raised $32 million in Series A funding, led by Avataar Ventures and India’s National Quantum Mission, to scale its full-stack quantum computing platform globally.
💸 Q.ANT has raised €62 million in Series A funding to commercialize its energy-efficient photonic processors for AI and high-performance computing.
⛓️ Quranium has partnered with Swiss cybersecurity firm Abatis to integrate real-time, tamper-proof endpoint protection into its quantum-secure Layer 1 blockchain infrastructure.
🧪 Matlantis Inc. has launched PFP Version 8, the first universal machine learning interatomic potential trained with high-accuracy r2SCAN datasets, doubling simulation precision while accelerating quantum materials discovery. With a new U.S. office in Cambridge, the company intends to expand collaborations across North America and support quantum tech R&D.
🧠 Google has launched a $100,000 research grant program to investigate whether quantum phenomena like entanglement and superposition influence brain function.
EVENTS.
Now -July 30 -- Womanium & WISER QUANTUM PROGRAM 2025. The 2025 Theme: Quantum solvers: algorithms for the world's hardest problems will be held Mondays & Wednesdays from 10:30 -12:00 ET. Register here.
Aug. 31– Sept. 5 -- IEEE Quantum Week 2025 will be held in Albuquerque, New Mexico.
Sept. 16-18 -- Quantum World Congress 2025 will be held at Capital One Hall in Greater Washington. The event is a chance for the world’s quantum ecosystem to come together and bring a quantum-ready future into focus.
Sept. 24-25 -- Q2B25 Paris at Cité des Sciences et de l’Industrie, Paris, France.
Sept. 29-Oct. 1 -- Quantum.Tech Europe is taking place in Rotterdam, Netherlands. The event will bring together the whole quantum supply chain to drive forward the commercial applications of Quantum Technologies.
Oct. 6-10 -- 8th International Conference for Young Quantum Information Scientists (YQIS25) will take place in Barcelona, Spain. YQIS is a conference series organized by and for PhD students and early-career researchers working across the broad field of quantum information.
Oct. 8 -- The Fifth Anniversary of The City Quantum & AI Summit will take place at the Mansion House in the City of London this year with the subtitle Race for Growth.
Oct. 13-17 -- Quantum Reference Frames 2025 will bring together leading experts on quantum reference frames and the many related subjects in the first focused event in the new era of quantum frame covariance. QRF 2025 is co-funded by the Quantum Information Structure of Spacetime consortium.
Oct. 19-21 -- Q+AI will be held in New York City. This event will uncover the coming wave of Quantum + AI, include 50+ speakers, daily mentoring sessions and 16 sessions, one continuous track.
Nov. 10-12 -- European Quantum Technologies Conference 2025 will be held at Øksnehallen, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Dec. 1-4 -- QUEST-IS 2025 Quantum Engineering Sciences and Technologies for Industry and Services From Quantum Engineering to Applications for Citizens. EDF Lab, Paris-Saclay, France.
How many qubits was today's newsletter? |